So, when we talk about ancient civilizations, we’re basically referring to these really interesting societies that existed a long time ago.
Think about it like this: you know how we have countries and cities today with their own governments, buildings, and cultures? Well, ancient civilizations were kind of like that, but way back in history.
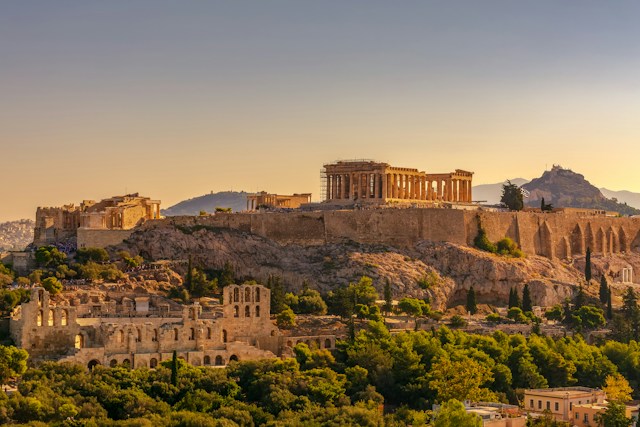
Imagine places like ancient Egypt with their massive pyramids, or ancient Greece with their philosophers and myths.
These civilizations were advanced for their time, building impressive structures, creating written languages, and coming up with all sorts of ideas and inventions that still impact us today.
It’s like taking a journey back in time to explore how people lived, what they believed, and how they shaped the world we live in now.
So, whenever we talk about ancient civilizations, we’re diving into this fascinating part of human history that’s full of stories, discoveries, and amazing achievements.
So be ready to dive into the list and uncover the secrets of our past
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is meant by ancient civilizations?

Ancient civilizations refer to complex societies that developed in various regions of the world during prehistoric and early historic times.
These civilizations emerged independently and exhibited advanced cultural, technological, economic, and social achievements.
Ancient civilizations typically possessed organized governments, sophisticated architectural structures, writing systems, religious beliefs, and complex social hierarchies.
Examples of ancient civilizations include Mesopotamia (Sumer, Babylon, Assyria), Ancient Egypt, the Indus Valley Civilization, Ancient China, Mesoamerica (Olmec, Maya, Aztec), and the civilizations of ancient Greece and Rome, among others.
The study of ancient civilizations provides insights into the origins and development of human societies and the foundations of modern civilization.
How many ancient civilizations are there in the world?
It’s a bit tricky to give an exact number because it depends on how you define “ancient civilization” and which time periods you’re considering. However, there were many ancient civilizations that developed independently around the world. Some of the most famous ancient civilizations include:

These are just a few examples, and there were many more ancient civilizations that emerged in different regions and time periods. Each civilization had its own unique culture, achievements, and contributions to human history.
What are the 3 famous ancient civilizations?
Identifying the “three major ancient civilizations” can vary depending on different perspectives and criteria, but typically, the following three are widely considered among the most influential:
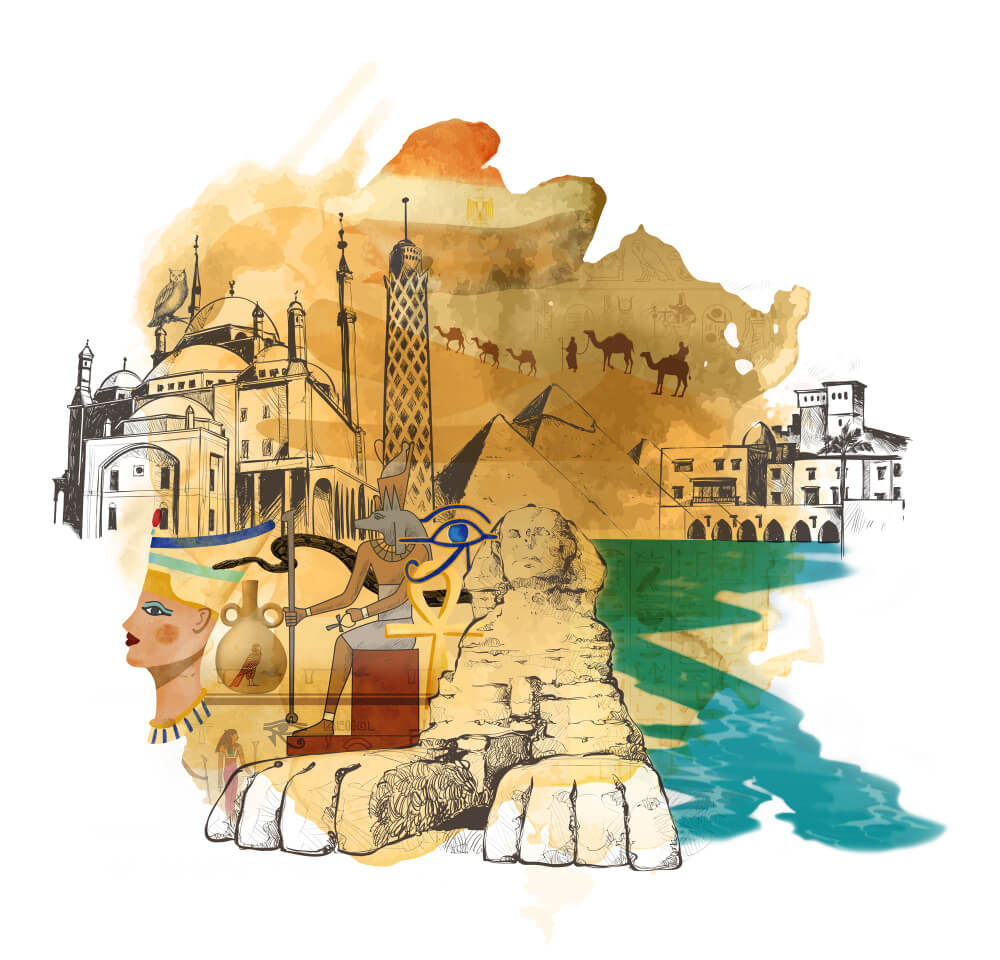
Ancient Egypt
Flourishing along the banks of the Nile River in northeastern Africa, ancient Egypt is renowned for its monumental architecture (such as the pyramids and temples), complex religious beliefs (including the worship of gods like Ra, Osiris, and Isis), hieroglyphic writing system, and powerful pharaonic dynasties that ruled for thousands of years.

1.Monumental Architecture:
Central to Ancient Egypt’s identity are its awe-inspiring architectural achievements, notably the pyramids, temples, and tombs. The Great Pyramid of Giza, built for Pharaoh Khufu, is a marvel of engineering and stands as the last surviving Wonder of the Ancient World. These monumental structures served religious, funerary, and administrative purposes, reflecting the Egyptians’ deep reverence for the afterlife and their divine rulers.
2.Rich Religious Beliefs:
The Egyptians worshipped a pantheon of gods and goddesses, each associated with specific attributes and responsibilities. From the sun god Ra to the goddess of fertility Isis, these deities were revered in elaborate temple complexes adorned with intricate hieroglyphic inscriptions and vibrant murals depicting mythological narratives.
3.Complex Hierarchical Society:
Ancient Egyptian society was hierarchically structured, with the pharaoh at the apex, followed by nobles, priests, scribes, artisans, and farmers. Social status was largely hereditary, and individuals’ roles were often determined by birthright. Despite this hierarchical order, there was social mobility, with individuals able to advance through education, skill, or military service.
4.Hieroglyphic Writing System:
The ancient Egyptians developed one of the earliest writing systems known as hieroglyphs, a complex script comprising pictorial symbols that represented objects, sounds, and concepts. Hieroglyphic inscriptions adorned temple walls, royal monuments, and funerary texts, providing invaluable insights into Egyptian history, religion, and culture.
5.Technological Innovations:
The Egyptians mastered the art of irrigation, harnessing the annual flooding of the Nile to cultivate crops and sustain a thriving agricultural economy. They also developed sophisticated techniques for quarrying stone, constructing monumental edifices, and embalming the dead for burial.
6.Enduring Legacy:
Though Ancient Egypt declined following foreign invasions and internal strife, its legacy endures as a cornerstone of human civilization. The decipherment of hieroglyphs in the early 19th century opened a window into Egypt’s ancient past, sparking renewed interest and scholarly exploration of this remarkable civilization.
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia, located in the region known as the Fertile Crescent between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers (in modern-day Iraq), was home to several ancient civilizations, including Sumer, Babylon, and Assyria. Mesopotamian civilizations made significant contributions to human history, including the development of writing (cuneiform script), the wheel, agriculture, mathematics, and early forms of law and government.
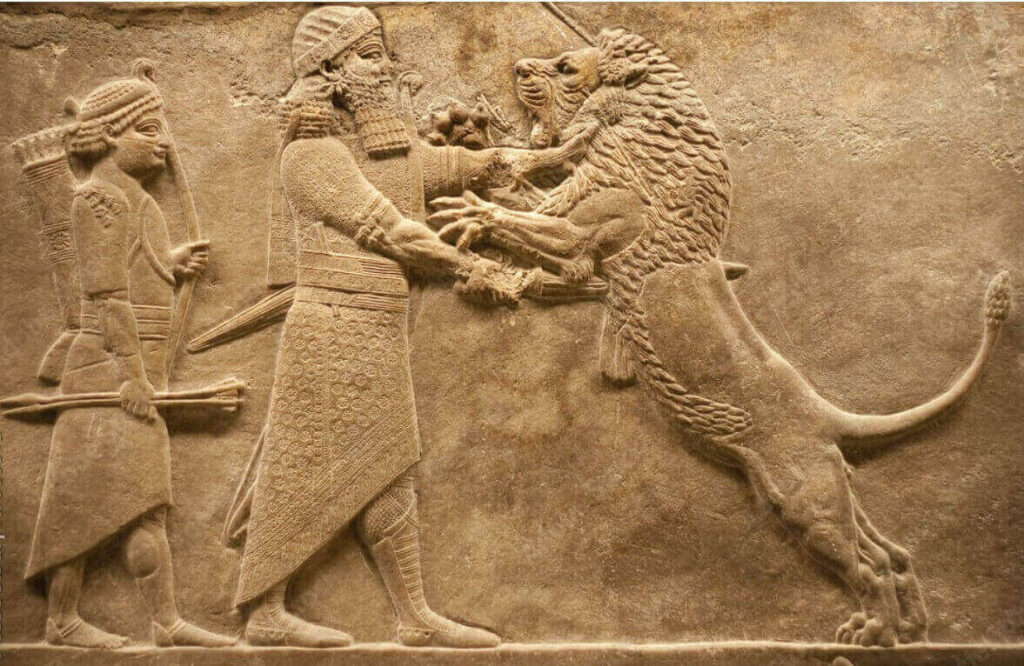

1. Emergence of Civilization:
Mesopotamia is one of the earliest known cradles of civilization, with evidence of human settlement dating back to the Neolithic period (around 10,000 BCE). The fertile soil and abundant water supply from the Tigris and Euphrates rivers provided favorable conditions for agriculture, leading to the rise of settled communities and the development of complex societies.
2. City-States and Urbanization:
Mesopotamia witnessed the emergence of some of the world’s first cities and urban centers. City-states such as Uruk, Ur, Lagash, and Babylon flourished along the riverbanks, becoming hubs of trade, governance, and culture. These cities featured monumental architecture, including ziggurats (temple towers), palaces, and defensive walls, reflecting the sophistication of Mesopotamian society.
3. Writing and Record-Keeping:
Developed around 3200 BCE, cuneiform consisted of wedge-shaped symbols impressed onto clay tablets using a stylus. This writing system was used for various purposes, including administrative records, economic transactions, legal documents, literature, and religious texts, enabling the preservation and dissemination of knowledge across generations.
4. Law and Governance:
The Code of Hammurabi, compiled by the Babylonian king Hammurabi around 1754 BCE, is one of the most well-known legal codes of ancient Mesopotamia. It codified laws and regulations governing various aspects of daily life, including commerce, property rights, marriage, and criminal justice.
5. Religion and Mythology:
Religion played a central role in Mesopotamian society, with polytheistic beliefs and a pantheon of gods and goddesses worshipped in temples and shrines. Mythological narratives, such as the Epic of Gilgamesh, provided insights into Mesopotamian cosmology, ethics, and human existence.
6. Technological and Scientific Advancements:
They developed sophisticated irrigation systems, including canals, dams, and levees, to harness the waters of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers for crop cultivation. They also made significant contributions to mathematics, including the development of the sexagesimal system of numerical notation and the calculation of areas and volumes.
7. Trade and Cultural Exchange:
Mesopotamia served as a crossroads of trade and cultural exchange, connecting the civilizations of the ancient Near East. Goods such as grain, textiles, metals, and luxury items were exchanged through overland and riverine trade routes, fostering economic prosperity and cultural diffusion. Mesopotamian cities became cosmopolitan centers, attracting merchants, artisans, and travelers from distant lands.
8. Decline and Legacy:
The region was conquered by various empires, including the Akkadian Empire, Babylonian Empire, Assyrian Empire, and Persian Empire. However, the legacy of Mesopotamia endures as a foundational chapter in the story of human history, influencing subsequent civilizations and shaping the development of art, literature, law, religion, and technology.
Ancient China
Ancient China emerged along the Yellow River (Huang He) and Yangtze River in East Asia and is renowned for its rich cultural heritage, including the invention of paper, gunpowder, printing, and the compass. Ancient Chinese civilizations, such as the Shang, Zhou, Qin, and Han dynasties, made enduring contributions to philosophy (Confucianism, Daoism), art (calligraphy, ceramics), literature (Confucian classics, poetry), and governance (imperial bureaucracy).
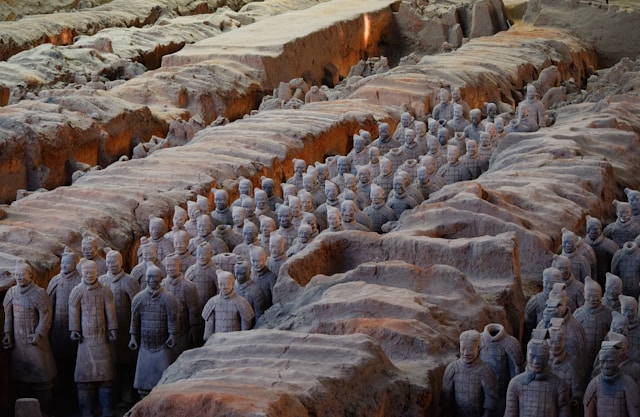

1. Geographic Context:
Ancient China emerged in East Asia, with its heartland situated along the Yellow River (Huang He) and the Yangtze River. The natural barriers of mountains and deserts provided protection from external invasions, while the fertile river valleys facilitated agricultural development and settlement.
2. Dynastic Succession:
Ancient China was ruled by a series of dynasties, each characterized by its own distinct political, social, and cultural developments. Key dynasties include the Xia, Shang, Zhou, Qin, Han, Tang, Song, Yuan, Ming, and Qing dynasties, spanning thousands of years of Chinese history.
3. Confucianism, Daoism, and Legalism:
Ancient China was shaped by diverse philosophical traditions, including Confucianism, Daoism (Taoism), and Legalism. Confucianism emphasized moral virtue, filial piety, and social harmony, while Daoism advocated for simplicity, naturalness, and harmony with the Dao (the Way). Legalism, on the other hand, promoted strict laws and centralized control to maintain social order and stability.
4. Great Wall and Imperial Palaces:
Ancient China is renowned for its architectural marvels, including the Great Wall, the Forbidden City, and the Summer Palace. The Great Wall, built over centuries of imperial rule, served as a defensive barrier against nomadic invasions from the north. The Forbidden City, located in Beijing, was the imperial palace complex of the Ming and Qing dynasties, while the Summer Palace served as a retreat for emperors during the hot summer months.
5. Silk Road and Trade:
Chinese silk, tea, porcelain, and other luxury goods were highly sought after by merchants from Europe, the Middle East, and Central Asia. The exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures along the Silk Road contributed to the flourishing of trade, diplomacy, and cultural exchange between East and West.
6. Technological Innovations:
Ancient China made significant technological advancements in various fields, including agriculture, metallurgy, papermaking, printing, and gunpowder. Inventions such as the plow, waterwheel, compass, and gunpowder revolutionized agriculture, navigation, warfare, and communication, laying the foundation for subsequent technological progress.
7. Literature, Art, and Philosophy:
Classic works such as the “Analects” of Confucius, the poetry of Li Bai and Du Fu, and the novels of the Ming and Qing dynasties reflect the depth and breadth of Chinese cultural expression.Ancient China produced a rich and diverse body of literature, art, and philosophy that continues to inspire and influence people worldwide.
8. Imperial Examination System:
This system allowed individuals to pursue careers in government based on their intellectual abilities rather than noble birth, promoting social mobility and administrative efficiency.
These three ancient civilizations are often considered major due to their significant contributions to human civilization, long-lasting legacies, and enduring influence on subsequent cultures and societies.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Why did ancient civilizations disappear?
The disappearance of ancient civilizations can be attributed to a variety of factors, often interconnected and complex:

Environmental Factors:
Changes in climate, such as prolonged droughts, floods, or other natural disasters, could disrupt agricultural systems, leading to food shortages and societal collapse. Deforestation, soil erosion, and depletion of natural resources could also contribute to environmental degradation, making regions less hospitable for human habitation.
Social and Political Instability:
Internal conflicts, civil unrest, and political instability could weaken civilizations from within. Ineffective governance, corruption, class conflicts, and social inequalities could further exacerbate societal tensions, leading to fragmentation and decline.
Economic Factors:
Economic mismanagement, trade disruptions, overreliance on unsustainable resources, and economic inequalities could undermine the stability and prosperity of ancient civilizations. Declines in trade networks, currency devaluation, and economic stagnation could lead to the unraveling of economic systems and societal collapse.
Epidemics and Disease:
Outbreaks of infectious diseases, such as plagues or pandemics, could devastate populations, weaken societal resilience, and disrupt economic and social structures. In the absence of effective medical knowledge or public health measures, epidemics could contribute to the decline and collapse of ancient civilizations.
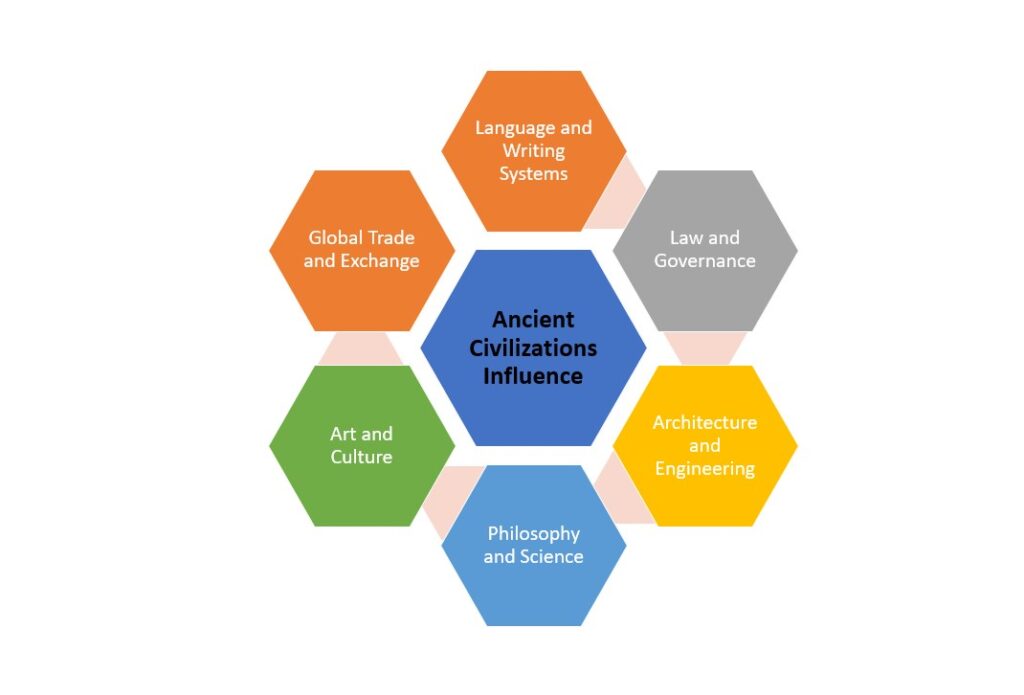
How did ancient civilizations influence us today?
Ancient civilizations have profoundly influenced modern societies in various ways, shaping our cultures, beliefs, technologies, and institutions.
Here are some key ways in which ancient civilizations continue to impact us today:
Overall, the disappearance of ancient civilizations was often the result of a combination of these factors, with each civilization facing its own unique set of challenges and circumstances that ultimately contributed to its decline and disappearance.
Why did ancient civilizations settle near rivers?
Ancient civilizations settled near rivers for various reasons.
Rivers provided a reliable water source for drinking, agriculture, and sanitation.
The fertile soil surrounding rivers allowed for bountiful crop cultivation, ensuring food security.
The availability of water, fertile land, transportation routes, defense advantages, and climatic benefits made river valleys attractive locations for the development of ancient civilizations.
Conclusion
Alright, friend, let’s wrap this up. We’ve covered a lot about ancient civilizations, from the pyramids of Egypt to the Great Wall of China. But here’s the bottom line: these ancient folks were onto something big.
Think about it: they built societies from scratch, faced challenges head-on, and left behind legacies that still blow our minds today. But here’s the kicker: they weren’t all sunshine and rainbows. They dealt with wars, famines, and all sorts of chaos, just like we do now.
So, what’s the takeaway? Simple. Learn from their successes and their failures. Take inspiration from their innovations and their resilience. And above all, remember that we’re part of a much bigger story—one that stretches back thousands of years.
So, keep digging into the past, my friend. Because the more we learn about ancient civilizations, the more we understand ourselves and the world around us. And that’s a journey worth taking, no matter where it leads.
If you have any questions? Kindly drop it in the comment section.


